} catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("오류가 발생했습니다 : "+e.getMessage());
}e는 변수다. 이 변수 앞의 Exception은 변수의 데이터 타입이 Exception이라는 의미다. Exception은 자바에서 기본적으로 제공하는 클래스로 java.lang에 소속되어 있다. 예외가 발생하면 자바는 마치 메소드를 호출하듯이 catch를 호출하면서 그 인자로 Exception 클래스의 인스턴스를 전달하는 것이다.
e.getMessage()는 자바가 전달한 인스턴스의 메소드 중 getMessage를 호출하는 코드인데, getMessage는 오류의 원인을 사람이 이해하기 쉬운 형태로 리턴하도록 약속되어 있다.
지금까지 API의 소비자로서 API 측에서 던지는 예외를 처리하는 방법을 알아봤다.
이번에는 API의 생산자로서 소비자들에게 API를 제공하는 입장에 서보자.
전 시간에 사용했던 코드를 바탕으로 이야기를 풀어가자.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception;
class Calculator{
int left, right;
public void setOprands(int left, int right){
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public void divide(){
try {
System.out.print("계산결과는 ");
System.out.print(this.left/this.right);
System.out.print(" 입니다.");
} catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("\n\ne.getMessage()\n"+e.getMessage());
System.out.println("\n\ne.toString()\n"+e.toString());
System.out.println("\n\ne.printStackTrace()");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class CalculatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator c1 = new Calculator();
c1.setOprands(10, 0);
c1.divide();
}
}위의 코드에서 예외가 발생한 이유는 10을 0으로 나누려고 하기 때문이다. 즉 setOprands를 통해서 입력된 두번째 인자의 값이 0이기 때문에 발생한 문제다. 우리가 할 수 있는 조치는 두가지다.
- setOprands의 두번째 인자로 0이 들어오면 예외를 발생시킨다.
- 메소드 divide를 실행할 때 right의 값이 0이라면 예외를 발생시킨다.
첫번째 방법을 적용해보자.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception;
class Calculator{
int left, right;
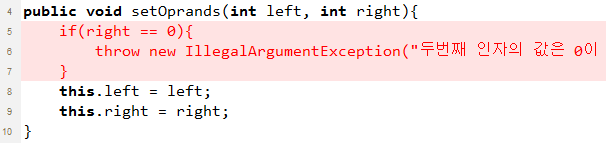
public void setOprands(int left, int right){
if(right == 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("두번째 인자의 값은 0이 될 수 없습니다.");
}
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public void divide(){
try {
System.out.print("계산결과는 ");
System.out.print(this.left/this.right);
System.out.print(" 입니다.");
} catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("\n\ne.getMessage()\n"+e.getMessage());
System.out.println("\n\ne.toString()\n"+e.toString());
System.out.println("\n\ne.printStackTrace()");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class CalculatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator c1 = new Calculator();
c1.setOprands(10, 0);
c1.divide();
}
}
차이점

실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: 두번째 인자의 값은 0이 될 수 없습니다.
at org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception.Calculator.setOprands(CalculatorDemo.java:6)
at org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception.CalculatorDemo.main(CalculatorDemo.java:27)두번째 인자의 값이 0이 되었을 때 setOprands의 사용자에게 예외 클래스인 IllegalArgumentException을 던지고 있다. 사용자인 main은 예외와 함께 '두번째 인자의 값은 0이 될 수 없습니다.'라는 메시지를 받게 되고 이 정보를 바탕으로 전달 값을 변경하게 된다.
아래와 같이 divide 내에서 예외를 처리할 수도 있다.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception;
class Calculator{
int left, right;
public void setOprands(int left, int right){
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public void divide(){
if(this.right == 0){
throw new ArithmeticException("0으로 나누는 것은 허용되지 않습니다.");
}
try {
System.out.print("계산결과는 ");
System.out.print(this.left/this.right);
System.out.print(" 입니다.");
} catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("\n\ne.getMessage()\n"+e.getMessage());
System.out.println("\n\ne.toString()\n"+e.toString());
System.out.println("\n\ne.printStackTrace()");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class CalculatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator c1 = new Calculator();
c1.setOprands(10, 0);
c1.divide();
}
}
차이점

throw는 인위적으로 예외를 발생시키는 명령이다.
throw 뒤에는 예외 정보를 가지고 있는 예외 클래스가 위치한다. 자바 가상 머신은 이 클래스를 기준으로 어떤 catch 구문을 실행할 것인지를 결정한다. 또 실행되는 catch 구문에서는 예외 클래스를 통해서 예외 상황의 원인에 대한 다양한 정보를 얻을 수 있다. 이 정보를 바탕으로 문제를 해결하게 된다.
필자가 사용한 예외인 IllegalArgumentException, ArithmeticException은 자바에서 기본적으로 제공하는 예외다. 이러한 예외들은 자바 가상머신이 사용하기도 하고 또 응용 프로그램 개발자가 사용할 수도 있다. 기본적으로 제공되는 어떤 예외들이 있는지를 파악하고 적당한 예외를 사용하는 것은 중요한 문제다. 클래스 Exception을 API 문서에서 찾아보고 그 하위 클래스로 어떤 것들이 있는지 살펴보는 것도 도움이 된다. 다음은 기억할만한 주요 Exception들의 리스트다. (effective Java p338 참고)
| 예외 | 사용해야 할 상황 |
| IllegalArgumentException | 매개변수가 의도하지 않은 상황을 유발시킬 때 |
| IllegalStateException | 메소드를 호출하기 위한 상태가 아닐 때 |
| NullPointerException | 매개 변수 값이 null 일 때 |
| IndexOutOfBoundsException | 인덱스 매개 변수 값이 범위를 벗어날 때 |
| ArithmeticException | 산술적인 연산에 오류가 있을 때 |
예외의 여러가지 상황들
예외에 대한 시야를 넓히기 위해서 몇가지 상황들을 간단한 코드로 만들어 보았다.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception;
class E{
void throwArithmeticException(){
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
}
문제없이 컴파일이 될 것이다. 이번엔 아래와 같이 코드를 바꿔보자.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception;
import java.io.IOException;
class E{
void throwArithmeticException(){
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
void throwIOException(){
throw new IOException();
}
}
차이점
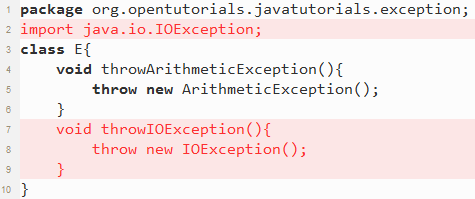
이번에는 컴파일 되지 않을 것이다. 에러 내용은 아래와 같다. 왜 그럴까?
src\org\opentutorials\javatutorials\exception\ThrowExceptionDemo2.java:8: error: unreported exception IOException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
throw new IOException();
^
1 error에러에는 아래와 같이 적혀있다.
unreported exception IOException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
즉 IOException은 try...catch하거나 throw 해야 한다는 뜻이다.
이상하다 ArithmeticException, IOException 모두 Exception이다. 그럼에도 불구하고 유독 IOException만 try...catch 혹은 throw 를 해야 한다는 뜻이다. 자바는 이 두개의 예외를 다른 방법으로 대하고 있는 것이다. 우선 아래와 같이 코드를 변경해서 에러를 없애자.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.exception;
import java.io.IOException;
class E{
void throwArithmeticException(){
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
void throwIOException1(){
try {
throw new IOException();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
void throwIOException2() throws IOException{
throw new IOException();
}
}
차이점

예제의 핵심은 IOException은 예외처리를 강제하고 있지만 ArithmeticException은 그렇지 않다 점이다. 그 이유를 알아보자.
'📌 java > java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| java - getClass() (0) | 2020.05.01 |
|---|---|
| java - Object 클래스 (0) | 2020.04.30 |
| java - throw & throws (0) | 2020.04.28 |
| java - 예외의 강제 (0) | 2020.04.28 |
| java - finally (0) | 2020.04.28 |